Learn About Diamond Certification Learn About Diamond CertificationWhat's in a Certificate? A diamond certificate, also called a diamond grading report, or diamond quality report.It is a report created by a gemologist, or gemologists, who have scrutinized the diamond and placed it under a microscope to analyze its dimensions, clarity, cut, color, finish, symmetry, and other characteristics. Certification is the key to selecting a quality diamond at the lowest price. Certification is your only assurance of quality. A diamond certification is a detailed diamond quality report issued by an accredited independent gemological laboratory. The most recognized gemological laboratories that provide certified diamond quality reports to the diamond and jewelry industry are listed below. Click on the links to learn details about each laboratory and report.
 Certifications verses appraisals: It is very important to understand that appraisals are often not as accurate as a certified diamond quality report performed by an independent gemological laboratory. Appraisals are only as accurate as the skill, knowledge and training of the appraiser. Certifications verses appraisals: It is very important to understand that appraisals are often not as accurate as a certified diamond quality report performed by an independent gemological laboratory. Appraisals are only as accurate as the skill, knowledge and training of the appraiser.There is currently no legal educational or training requirements one must have to appraise diamonds or jewelry. Appraisals can be done by anyone, even someone with no training. Appraisals are often done by the salesperson selling the diamond. If you read the fine print, virtually all appraisals include legal disclaimers to protect the appraiser from legal recourse if the appraisal is inaccurate. Disclaimers usually state the appraisal is no guarantee of quality and is only the opinion of the appraiser. Many people who buy uncertified diamonds usually pay to much. What often appears to be a unbelievable low price usually turns out to be a diamond that has been inaccurately graded. It is not uncommon for a diamond appraisal to be inaccurate by two, three or more grades when the diamond is sent to G.I.A. for accurate evaluation. The quality of the certified diamond reports can vary somewhat depending on which gemological laboratory that performs the analysis and certification. It is important to be understand that grading accuracy is not always consistent between gemological laboratories. The color and clarity grading of diamonds are assigned by highly trained Graduate Gemologists using there individual subjective judgment skills to assign the proper diamond grades during analysis. Because of individual judgment some inconsistencies may occur in assigning quality grades. These inconsistencies are often the result of diamonds which are on the line between two grades. Fortunately diamonds are rarely vary more than one grade between gemological laboratories. The primary geological laboratories that provide certified quality reports are described below.  G.I.A. - The Gemological Institute of America: G.I.A. is the most well known and respected laboratory in the world. The division of G.I.A. which is responsible for the certification of diamonds is G.I.A.'s Gem Trade Laboratory. The G.I.A. diamond quality report provides a carefully drawn plot which illustrates the exact position, size and shape of every internal inclusion and external blemish a diamond possesses. G.I.A. is extremely strict in assigning color and clarity grades. If a diamonds quality is on the line of the next higher quality grade G.I.A. will usually always assign the lower grade. G.I.A. uses a Sarin proportion analyzer, a computer electronic measuring device to determine diamond proportions. Sun Jewelry recommends selecting a diamond with a G.I.A. Diamond Report or A.G.S. Diamond Certification for the best comparison of diamond quality. The cost of a G.I.A. or A.G.S. diamond quality report is $100 to $200. G.I.A. has recently added a new Dossier certification, a miniature version of the standard full G.I.A. diamond quality report except it does not provide the plot that shows inclusion and blemishes. However, G.I.A. does laser inscribe the edge or girdle of the submitted diamond with the G.I.A. diamond quality report number for identification purposes. The Dossier diamond quality report is primarily used on smaller diamonds because it is lower in cost. G.I.A. - The Gemological Institute of America: G.I.A. is the most well known and respected laboratory in the world. The division of G.I.A. which is responsible for the certification of diamonds is G.I.A.'s Gem Trade Laboratory. The G.I.A. diamond quality report provides a carefully drawn plot which illustrates the exact position, size and shape of every internal inclusion and external blemish a diamond possesses. G.I.A. is extremely strict in assigning color and clarity grades. If a diamonds quality is on the line of the next higher quality grade G.I.A. will usually always assign the lower grade. G.I.A. uses a Sarin proportion analyzer, a computer electronic measuring device to determine diamond proportions. Sun Jewelry recommends selecting a diamond with a G.I.A. Diamond Report or A.G.S. Diamond Certification for the best comparison of diamond quality. The cost of a G.I.A. or A.G.S. diamond quality report is $100 to $200. G.I.A. has recently added a new Dossier certification, a miniature version of the standard full G.I.A. diamond quality report except it does not provide the plot that shows inclusion and blemishes. However, G.I.A. does laser inscribe the edge or girdle of the submitted diamond with the G.I.A. diamond quality report number for identification purposes. The Dossier diamond quality report is primarily used on smaller diamonds because it is lower in cost.
 A.G.S. - American Gem Society (DQR) Diamond Quality Report ,and (DQD) Diamond Quality Document are the best certified diamond quality report available today. The A.G.S. gemological laboratory is equal or more strict than G.I.A. The A.G.S. diamond quality report also provides a carefully drawn plot which illustrates the exact position, size and shape of every internal inclusion and external blemish a diamond possesses. The diamond quality report provides a complete full analysis of diamond proportion, color and clarity. The A.G.S. is the only gemological laboratory that assigns a cut grade as a numerical value between 0 and 10. The AGS system of defining cut grade is modeled after the Towkowsky theoretical ideal brilliant which is a standard of ideal proportions and facet angles that were mathematically calculated by Marcel Tolkowsky in 1919. It also carefully considers important aspects of diamond polish and symmetry in the assignment of a cut grade. An ideal cut diamond is assigned A.G.S. cut grade 0. Small incremental proportion deviations from the ideal cut model assign the next higher numerical cut grade. Cut grades 1 and 2 are still considered very fine. Fewer diamonds are available with AGS diamond quality reports. AGS quality reports are most often used by diamond cutters who wish to confirm near ideal or ideal cut diamonds. The A.G.S. grading laboratory director is Peter Yantzer, past founding director of G.I.A.'s Gem Trade Laboratory. The A.G.S. was founded by Robert Shipley the founder of G.I.A. A.G.S. - American Gem Society (DQR) Diamond Quality Report ,and (DQD) Diamond Quality Document are the best certified diamond quality report available today. The A.G.S. gemological laboratory is equal or more strict than G.I.A. The A.G.S. diamond quality report also provides a carefully drawn plot which illustrates the exact position, size and shape of every internal inclusion and external blemish a diamond possesses. The diamond quality report provides a complete full analysis of diamond proportion, color and clarity. The A.G.S. is the only gemological laboratory that assigns a cut grade as a numerical value between 0 and 10. The AGS system of defining cut grade is modeled after the Towkowsky theoretical ideal brilliant which is a standard of ideal proportions and facet angles that were mathematically calculated by Marcel Tolkowsky in 1919. It also carefully considers important aspects of diamond polish and symmetry in the assignment of a cut grade. An ideal cut diamond is assigned A.G.S. cut grade 0. Small incremental proportion deviations from the ideal cut model assign the next higher numerical cut grade. Cut grades 1 and 2 are still considered very fine. Fewer diamonds are available with AGS diamond quality reports. AGS quality reports are most often used by diamond cutters who wish to confirm near ideal or ideal cut diamonds. The A.G.S. grading laboratory director is Peter Yantzer, past founding director of G.I.A.'s Gem Trade Laboratory. The A.G.S. was founded by Robert Shipley the founder of G.I.A.
 E.G.L. - The European Gemological Laboratory: E.G.L. provides a detail diamond report that is sometimes not as strict as G.I.A. Because the art of diamond grading is a subjective science, two different gemological laboratories may arrive at differing opinions when assigning a diamonds color and clarity grade. E.G.L. has sometimes been known to assign a higher grade on diamonds that have grades on the border between two grades. G.I.A. usually will always give the lower grade. When purchasing a diamond with an E.G.L. quality report, it is possible to receive a lower grade if it is submitted to G.I.A. for a new diamond quality report. Diamonds with E.G.L. quality reports that are offered for prices significantly lower than equal quality G.I.A. certified diamonds have the greatest chance of not matching if submitted to G.I.A. for a new quality report. E.G.L. certifications are often reliable but one must be aware of possible inconsistencies and limitations when comparing diamond certifications between different gemological laboratories E.G.L. - The European Gemological Laboratory: E.G.L. provides a detail diamond report that is sometimes not as strict as G.I.A. Because the art of diamond grading is a subjective science, two different gemological laboratories may arrive at differing opinions when assigning a diamonds color and clarity grade. E.G.L. has sometimes been known to assign a higher grade on diamonds that have grades on the border between two grades. G.I.A. usually will always give the lower grade. When purchasing a diamond with an E.G.L. quality report, it is possible to receive a lower grade if it is submitted to G.I.A. for a new diamond quality report. Diamonds with E.G.L. quality reports that are offered for prices significantly lower than equal quality G.I.A. certified diamonds have the greatest chance of not matching if submitted to G.I.A. for a new quality report. E.G.L. certifications are often reliable but one must be aware of possible inconsistencies and limitations when comparing diamond certifications between different gemological laboratoriesThe E.G.L. certification however does provide more proportion information than the G.I.A. diamond report by including the important pavilion and crown angles in their diamond report. Be aware that plots of internal and external blemishes on E.G.L. certifications are much less detailed than G.I.A. or A.G.S. quality reports. Many diamonds under one carat in size are are certified by E.G.L. due to the benefit of lower cost and faster service. E.G.L. also provides a economically priced miniature version of its full certification.
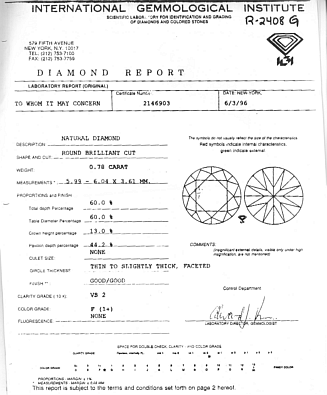
 I.G.I. - The International Gemological Institute: I.G.I. provides a detailed certification that is not as strict as G.I.A. Like the E.G.L. the I.G.I. certification also provides more information than the G.I.A. diamond report by including the important pavilion and crown angles in their diamond report. Diamond grades rarely vary over one grade from G.I.A. Like E.G.L., I.G.I.'s diamond report cost less and is used mostly by diamond cutters for smaller diamonds although larger diamonds are also available. You must be aware that diamonds graded by E.G.L and I.G.I. can be less in price than diamonds graded equal by G.I.A. and may sometimes not match G.I.A. if resubmitted. I.G.I. - The International Gemological Institute: I.G.I. provides a detailed certification that is not as strict as G.I.A. Like the E.G.L. the I.G.I. certification also provides more information than the G.I.A. diamond report by including the important pavilion and crown angles in their diamond report. Diamond grades rarely vary over one grade from G.I.A. Like E.G.L., I.G.I.'s diamond report cost less and is used mostly by diamond cutters for smaller diamonds although larger diamonds are also available. You must be aware that diamonds graded by E.G.L and I.G.I. can be less in price than diamonds graded equal by G.I.A. and may sometimes not match G.I.A. if resubmitted.
|